The Science of a JAK Inhibitor in Psoriatic Arthritis
MAY 4, 2022
Upadacitinib: A Selective JAK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Active Psoriatic Arthritis
PsA is a heterogeneous inflammatory disease that is characterized by multiple disease domains, including peripheral arthritis, skin psoriasis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and axial disease.1
Despite the current available treatments, including: csDMARDs such as MTX; bDMARDs such as TNF, IL-17, and IL-12/23 inhibitors; or tsDMARDs such as tofacitinib or apremilast, many patients with PsA cannot achieve comprehensive control of their symptoms.2
On December 14, 2021, the FDA approved the use of upadacitinib (UPA) for the treatment of adults with active PsA who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers. Use of UPA in combination with other JAK inhibitors, bDMARDs, or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended. The recommended dose of UPA for PsA is 15 mg QD.3
Highlighted below are results from the two Phase 3 clinical trials that evaluated UPA in patients with PsA.2,4
bDMARD=biologic DMARD; csDMARD=conventional synthetic DMARD; DMARD=disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; FDA=US Food and Drug Administration; IL=interleukin; JAK=Janus kinase; MTX=methotrexate; PsA=psoriatic arthritis; QD=once daily; TNF=tumor necrosis factor; tsDMARD=targeted synthetic DMARD.
1. Coates LC, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(5):1060-1071.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
3. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
4. McInnes IB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1227-1239.
OVERVIEW OF THE SELECT PHASE 3 TRIAL PROGRAM IN PSA1-5
The safety and efficacy of UPA 15 mg QD were evaluated for the treatment of PsA in 2 randomized Phase 3 clinical trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2.

aUPA 30 mg QD is not an approved dosing regimen.
bAt week 24, patients receiving PBO were switched in a blinded manner either to UPA 15 mg QD or UPA 30 mg QD.
cFull analysis set (nonresponder imputation). All primary analyses were controlled for multiple comparisons.
†Statistically significant in the multiplicity-controlled analysis.
ACR20=American College of Rheumatology criteria for 20% improvement; ADA=adalimumab; EOW=every other week; IR=inadequate response; OLE=open-label extension; PBO=placebo.
1. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
2. McInnes IB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1227-1239.
3. Supplement to: McInnes IB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1227-1239.
4. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
5. Supplement to: Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.

IN SELECT-PSA 2 (BDMARD-IR), A SIGNIFICANTLY GREATER PROPORTION OF PATIENTS ACHIEVED MINIMAL DISEASE ACTIVITY AT WEEK 24 WHEN TREATED WITH UPA 15 MG VS PBO


1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):903-919.
3. Data on File. AbbVie. ABVRRTI72463.
4. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
5. Supplement to: Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.

ACR20/50/70 RESPONSE RATES THROUGH WEEK 56 IN PATIENTS TREATED WITH UPA 15 MG (SELECT-PSA 2; BDMARD-IR)

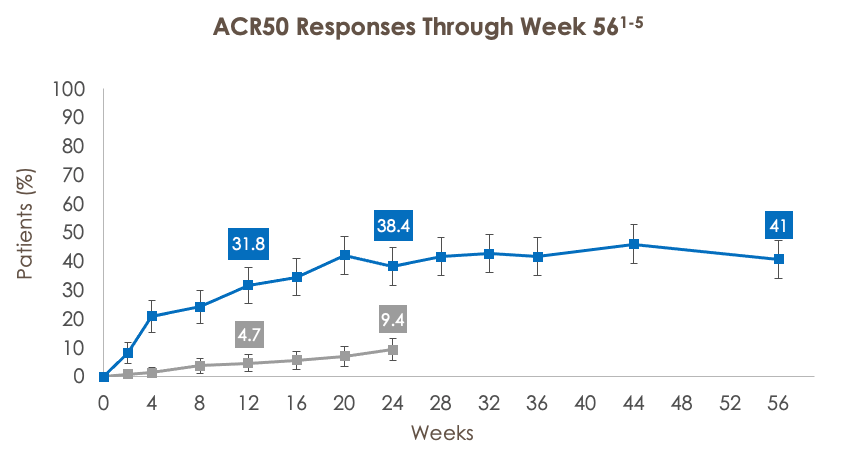
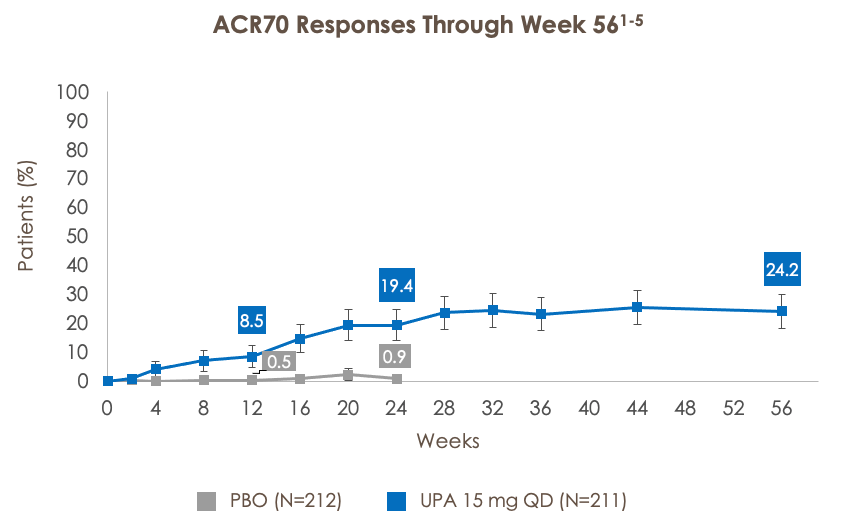
ACR50=American College of Rheumatology criteria for 50% improvement; ACR70=American College of Rheumatology criteria for 70% improvement.
***p<0.001 for UPA vs PBO. †Statistically significant in the multiplicity-controlled analysis.
Full analysis set (nonresponder imputation). ACR20 at week 12 (UPA vs PBO) was a primary endpoint and was controlled for multiplicity. All other analyses were additional endpoints and were not controlled for multiple comparisons.
1. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
3. Supplement to: Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
4. Mease PJ, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):903-919.

IN SELECT-PSA 2 (BDMARD-IR), TREATMENT WITH UPA 15 MG RESULTED IN IMPROVEMENTS IN SKIN MANIFESTATIONS OF PSA, AND IN IMPROVEMENTS IN ENTHESITIS AND DACTYLITIS IN PATIENTS WITH PRE-EXISTING ENTHESITIS AND DACTYLITIS:

aEvaluated in patients with BSA ≥3% at baseline.
***p<0.001 for UPA vs PBO. †Statistically significant in the multiplicity-controlled analysis.
Full analysis set (nonresponder imputation). PASI 75 at week 16 (UPA vs PBO) was a key ranked secondary endpoint and was controlled for multiplicity. All other analyses were additional endpoints and were not controlled for multiple comparisons; nominal p-values are provided.
BSA=body surface area; PASI 75=75% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score; PASI 90=90% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PASI 100=100% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score.
1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):903-919.
3. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.

aFor patients with LEI >0 at baseline; resolution of enthesitis defined as LEI=0.
***p<0.001 for UPA vs PBO.
Full analysis set (nonresponder imputation). Resolution of enthesitis at week 12 (UPA vs PBO) was an exploratory endpoint and was not controlled for multiplicity.
1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):903-919.

aFor patients with LDI >0 at baseline; resolution of dactylitis defined as LDI=0.
***p<0.001 for UPA vs PBO.
Full analysis set (nonresponder imputation). Resolution of dactylitis at week 12 (UPA vs PBO) was an exploratory endpoint and was not controlled for multiplicity.
LDI=Leeds Dactylitis Index.
1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
2. Mease PJ, et al. Rheumatol Ther. 2021;8(2):903-919.


aExcluding TB and herpes zoster.
bExcluding NMSC.
cOne event of abnormal lymphocyte morphology was reported in the UPA 15 mg arm of SELECT-PsA 2; per investigator, no further diagnosis was made.
dVTE includes DVT and PE.
eMACE is defined as CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke.
hIncludes treatment-emergent and non-treatment-emergent deaths.

aIncludes two Phase 3 studies (cutoff date: June 30, 2020).
bIncludes UPA monotherapy and combination therapy with csDMARDs across six Phase 3 studies (cutoff date: June 30, 2020).
cExcluding TB, oral candidiasis, and herpes zoster.
dExcluding NMSC.
eIn the UPA 15 mg arm of SELECT-PsA 2, one event of abnormal lymphocyte morphology was reported in the 24-week analysis and two events in the 56-week analysis; per investigators, no further diagnoses were made.
fVTE includes DVT and PE.
gMACE is defined as CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and nonfatal stroke.

CV=cardiovascular; DVT=deep vein thrombosis; E=event; GI=gastrointestinal; MACE=major adverse cardiovascular event; NMSC=nonmelanoma skin cancer; PE=pulmonary embolism; PY=patient-year; RA=rheumatoid arthritis; TB=tuberculosis; TEAE=treatment emergent adverse event; VTE=venous thromboembolic event.
1. Data on File. AbbVie. ABVRRTI71873.
2. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
3. Cohen SB, et al. Poster POS0220. EULAR 2021 E-Congress; June 2-5, 2021.
4. Burmester GR, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:1287-1288.
5. Data on File. AbbVie. ABVRRTI71618.

SUMMARY

1. RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
2. McInnes IB, et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1227-1239.
3. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;80(3):312-320.
4. Burmester GR, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:1287-1288.
UPADACITINIB PRESCRIBING CONSIDERATIONS FOR PSA

ALC=absolute lymphocyte count; ANC=absolute neutrophil count.
RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
Upadacitinib Indications & IMPORTANT SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS AND BOXED WARNINGS
INDICATIONS
Psoriatic Arthritis:
Upadacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with active psoriatic arthritis who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Upadacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use for RA and PsA: Use of upadacitinib in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic DMARDs, or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
IMPORTANT SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS AND BOXED WARNINGS
Serious Infections
Patients treated with upadacitinib are at increased risk for developing serious infections that may lead to hospitalization or death.
These infections include TB, invasive fungal, bacterial, viral, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens.
Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants, such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Test for latent TB before and during therapy; treat latent TB prior to use. Consider the risks and benefits prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection. If a serious infection develops, interrupt upadacitinib until the infection is controlled.
Mortality
In a postmarketing safety study in RA patients ≥50 years of age with at least one CV risk factor comparing another JAK inhibitor to TNF blockers, a higher rate of all cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, was observed with the JAK inhibitor.
Malignancies
Malignancies have been observed in upadacitinib treated patients. In RA patients treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of lymphomas and lung cancers was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk. Consider the benefits and risk for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with upadacitinib, particularly in patients with a known malignancy(other than a successfully treated non-melanoma skin cancer), patients who develop a malignancy when on treatment, and patients who are current or past smokers.
Major adverse cardiovascular events
In RA patients who were ≥50 years of age with at least one CV risk factor treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of MACE (CV death, myocardial infarction, and stroke) was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk. Consider benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with upadacitinib. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur. Discontinue upadicitinib in patients that have experienced a myocardial infarction or stroke.
Thrombosis
Thrombosis, including deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thrombosis, has occurred in patients treated with JAK inhibitors, including upadacitinib. Many of these adverse events were serious and some resulted in death. In RA patients who were ≥50 years of age with at least one CV risk factor treated with another JAK inhibitor, a higher rate of thrombosis was observed when compared with TNF blockers. Avoid upadacitinib in patients at risk. Patients with symptoms of thrombosis should discontinue upadacitinib and be promptly evaluated.
Other Serious Adverse Reactions
Patients treated with upadacitinib also may be at risk for other serious adverse reactions, including GI perforations, neutropenia, lymphopenia, anemia, lipid elevations, liver enzyme elevations, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Vaccinations
Use of live, attenuated vaccines during, or immediately prior to, upadacitinib therapy is not recommended. Prior to initiating upadacitinib, it is recommended that patients be brought up to date with all immunizations in agreement with current immunization guidelines.
Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥1%) in patients treated with upadacitinib were upper respiratory tract infections, herpes zoster, herpes simplex, bronchitis, nausea, cough, pyrexia, and acne.
RINVOQ® (upadacitinib) [package insert]. North Chicago, IL: AbbVie Inc.; 2022.
Review accompanying upadacitinib full Prescribing Information for additional information, visit www.rxabbvie.com
or contact AbbVie Medical Information at 1-800-633-9110.
Content developed by AbbVie Inc. This content is intended for US/PR Health Care Professionals. The US Medical Affairs department of AbbVie Inc. is the copyright owner of this presentation and has paid Consultant360 to host this content.
AbbVie is solely responsible for all written content within this presentation ©2022
AbbVie Inc. All rights reserved.
AbbVie Inc. JAKa-US-000032-MC Approval Date: 05/2022 v1.0


